Running ads that make you wonder if anyone’s even clicking? Yep, we’ve been there. It’s time to ditch the guesswork and dive into a PPC strategy that’s built for small businesses and e-commerce stores like yours. Think real results. Think sales—not just clicks. This guide? It’s your roadmap to doing PPC the smart way. Ready to make it happen? Let’s roll.
Understanding the Basics of PPC Campaigns
Before we jump into the setup, let’s cover the basics. PPC (Pay-Per-Click) is a model of internet marketing where advertisers pay a fee each time one of their ads is clicked. It’s essentially buying visits to your site, rather than organically earning them.
For small businesses and e-commerce stores, it’s a fantastic way to generate traffic fast—especially when trying to reach a targeted audience. Platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and Amazon Ads are prime examples of where you can run PPC campaigns. Each of these platforms offers unique advantages, depending on your business goals.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the different types of PPC ads:
- Search Ads: These are text ads that appear in search engine results pages (SERPs). Great for targeting specific keywords.
- Display Ads: Visual-based ads that appear across websites in the Google Display Network.
- Shopping Ads: Product-based ads that appear in search engine shopping tabs.
- Video Ads: Ads that run on video platforms, like YouTube, and can drive high engagement.
PPC campaigns offer flexibility in how you reach your audience. Whether you want your ads to show up on a search engine results page (SERP), across a variety of websites in the Display Network, or in a user’s social media feed, PPC can get your brand in front of the right people at the right time.
Step 1: Setting Up Your PPC Campaign – The Right Way
Defining Your Campaign Goals
Every successful PPC campaign starts with well-defined goals. If you’re an e-commerce store, your primary goal might be to increase sales. For service-based small businesses, you might want to generate leads or drive traffic to your site. Establishing clear objectives helps guide your decision-making process throughout the campaign setup.
For example, let’s say you own a yoga studio and want to run a PPC campaign. Your objective might be to increase class bookings. In this case, you’d set up a campaign with conversion-focused objectives, aiming for people to fill out a booking form or call your studio.
Selecting the Right PPC Platform
Choosing the right platform depends on your target audience. Here’s a quick comparison of three major platforms:
- Google Ads: Best for businesses looking to target high-intent users. If you run a plumbing business, people searching for “emergency plumber near me” are likely in immediate need of your service, and Google Ads can place your ad at the top of their search results.
- Facebook Ads: Perfect for businesses focused on audience targeting and brand awareness. If you’re promoting a clothing line, Facebook allows you to target users based on their interests in fashion and shopping habits.
- Amazon Ads: If you’re selling products on Amazon, this platform is a no-brainer. For example, if you sell electronics, Amazon Ads can promote your product listings to users already searching for “best wireless earbuds.”
Creating Your Ad Account
These are the basic steps to get started, but if you’re aiming for a High Return on Ad Spend (ROAS), getting expert help from a digital marketing agency like Kaizen Digital Studios can make all the difference.
Here’s how to get started with Google Ads:
- Go to ads.google.com.
- Set up a Google account if you don’t already have one.
- Fill in your business information, set up billing, and payment methods.
- Choose your campaign goals (traffic, sales, leads, etc.) and follow the prompts to create your first campaign.
Other platforms, like Facebook and Amazon, follow similar account setup procedures, so you’ll have a consistent process across platforms.

Keyword Research and Structuring Your Ad Groups
Effective keyword research is at the core of any successful PPC campaign. Using tools like Google Keyword Planner, Moz, SEMrush, or Ahrefs, you can find keywords that are relevant to your business.
Let’s imagine you run a home décor e-commerce store. Keywords like “affordable home décor” or “modern furniture” may have high search volumes. However, broad keywords can be competitive and expensive. You’ll need to find a balance between high-traffic and low-competition keywords to make the most of your ad budget.
Grouping Keywords Effectively
Once you’ve done your research, group your keywords into ad groups based on their relevance. For instance, if you’re promoting different categories of home décor (e.g., lighting, furniture, or wall art), each ad group should contain keywords related to one of those categories. This ensures that the ad shown to the user is closely related to what they’re searching for.
Example:
- Ad Group 1: “Modern Living Room Lighting,” “Chandeliers for Living Rooms,” “LED Floor Lamps”
- Ad Group 2: “Contemporary Sofas,” “Sectional Sofas for Small Spaces,” “Leather Recliners”
Negative Keywords
Negative keywords help you avoid spending money on irrelevant clicks. For instance, if you’re a premium furniture store, you wouldn’t want to attract people searching for “cheap furniture” or “free delivery furniture.” Adding “cheap” and “free delivery” to your negative keywords ensures you won’t waste money on irrelevant traffic.

Your ad copy is the first thing people see, so it needs to grab attention and deliver value quickly. Whether it’s Google Ads or Facebook Ads, your copy should include:
- A strong headline that speaks to the user’s needs.
- A clear call to action (CTA), such as “Shop Now” or “Get a Free Quote.”
Example:
Let’s say you own a bakery, and you’re promoting your online cake orders:
- Headline: “Order Custom Cakes for Any Occasion”
- Description: “Free Delivery Available. Choose from a Variety of Flavors and Designs. Click to Customize Yours!”
A/B Testing
Always run A/B tests to find out which version of your ad works best. One ad might focus on price (‘20% off all cakes!’), while another might highlight quality (‘Handcrafted cakes, delivered to your door’). Testing different messages helps you learn what resonates with your audience.
Landing Page Optimisation
An optimised landing page can make or break your campaign’s success. Ensure the page users land on after clicking your ad is directly relevant to the ad copy. If your ad promises “20% off all cakes,” your landing page should feature this offer prominently, ideally with a clear CTA like “Shop Now.”
Example: If your bakery ad leads people to a generic homepage, they may feel disconnected from the offer and leave the site. But a specific landing page showing all the cakes available with the discount offer creates a smooth and cohesive experience that’s more likely to result in a sale.

Setting Your PPC Budget and Bidding Strategy
Deciding on a budget can be daunting, but the key is to start small and scale as you see results. If you’re running a Google Ads campaign, you might set a daily budget of $10 and test different ad groups. Over time, you can increase spending on the highest-performing groups.
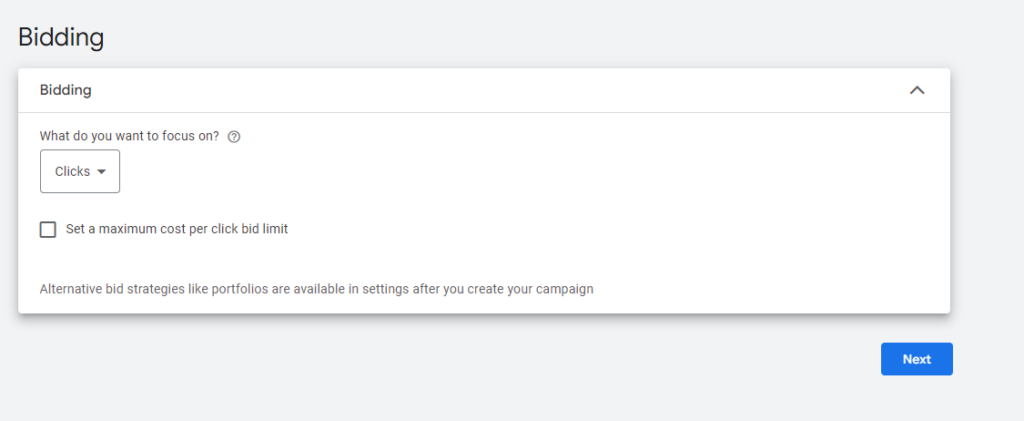
Bidding Strategies
There are two main types of bidding strategies in Google Ads:
- Manual Bidding: You set a maximum bid for each keyword. This is a great option if you want full control over how much you spend per click.
- Automated Bidding: Google automatically adjusts your bids based on how likely a click is to result in a conversion. This can save time and help optimise results, but you’ll need to monitor performance to ensure costs don’t get too high.
For example, if you’re targeting keywords like “emergency plumbing services,” which are highly competitive, you might want to experiment with automated bidding to get the best placements without overpaying for clicks.
Scaling Your Budget
Once you identify which ads are driving conversions, you can allocate more budget to them. For example, if an ad for “luxury sofas” is outperforming your ad for “affordable chairs,” you can shift more of your budget to the high-performing ad group.
Tracking and Conversion Optimisation
To measure your campaign’s success, you need to set up conversion tracking. This helps you see how many clicks result in a desired action, like filling out a contact form or making a purchase.
Google Ads allows you to track specific conversions, like when someone buys something from your online store or signs up for your newsletter. If you own a travel agency, you might track how many clicks on your “Book Now” button result in completed bookings.
Monitoring Key Metrics
Pay attention to these critical metrics:
- CTR (Click-Through Rate): This measures how often people click on your ad after seeing it. A high CTR indicates your ad copy is resonating with your audience.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of clicks that result in a sale or other desired action.
- CPC (Cost Per Click): How much you’re spending on average for each click. If your CPC is too high and conversion rates are low, you may need to optimise your ad copy or landing page.
Optimising for Conversions
Aligning your ad copy, targeting, and landing pages with your conversion goals will lead to better results. Consider running A/B tests to optimise these elements continuously.
Cross-Platform PPC Strategies
Running PPC campaigns across Google, Facebook, and Amazon allows you to reach a broader audience and gain deeper insights. A cross-platform strategy can help optimise your campaign performance by spreading your reach and using data from one platform to improve another.
Integrating PPC with SEO and Social Media
PPC works best when combined with other digital marketing efforts. For instance, PPC can drive traffic to a well-optimised website (SEO), while social media campaigns can complement paid advertising by building brand awareness.

Advanced Ad Optimisation Techniques for Long-Term Success
Once your campaign is up and running, it’s crucial to keep optimising it over time. PPC advertising isn’t a “set-it-and-forget-it” tactic. Constantly evaluating and refining your ads ensures they perform better, waste less money, and ultimately drive higher ROI.
Ad Rotation and Testing
Even after your campaign is live, keep testing different ads to see what works best. A tool like Google’s Responsive Search Ads lets you test different headlines and descriptions to figure out the winning combination. For instance, you might have two headlines in mind for an ad: “Get Organic Cat Food Delivered” versus “Buy Premium Pet Food Now.” Run both for a few weeks to see which one gets a better click-through rate (CTR).
Tools like Google’s Responsive Search Ads allow you to enter multiple headlines and descriptions, and Google will automatically test different combinations. This helps identify which versions drive the best results.
Bid Adjustments
As you gather data, you’ll notice that some keywords perform better than others. It’s essential to make bid adjustments based on this data. For instance, if a particular keyword is driving high conversions but costs less per click, consider increasing your bid to capture more traffic from that keyword.
Additionally, adjusting your bids for different times of the day or week can significantly improve performance. For example, if your online store gets more sales during weekends, it makes sense to allocate more budget for ads during that period.
Refining Audience Targeting
As your campaign matures, you’ll gain insights into your audience’s behaviour, allowing you to refine your targeting. If you run a luxury skincare business, you might discover that users in certain age groups or income brackets respond better to your ads. You can use this information to narrow your audience to higher-value prospects and exclude users who are less likely to convert.
On platforms like Facebook Ads, you can also use lookalike audiences—audiences similar to your existing customers based on key attributes like interests and behaviours. For instance, a business selling fitness equipment can target individuals who closely resemble their top customers in terms of engagement and purchase history.
Geotargeting and Device Targeting
If your business serves local customers or specific regions, you should adjust your campaign’s geotargeting settings. For instance, a law firm operating in Sydney should focus its ad spend on users in that region, avoiding wasted clicks from users in other areas.
Similarly, device targeting allows you to tailor ads for mobile versus desktop users. If you’re promoting a mobile app, focus on mobile users to drive app downloads. On the other hand, a SaaS platform offering complex software may see better results targeting desktop users, as they are more likely to engage with longer forms or detailed product pages.

Retargeting and Remarketing Tactics
Retargeting allows you to reach users who have already visited your site. By showing these users tailored ads, you can remind them to complete their purchase or explore your offerings further. Remarketing is particularly useful for e-commerce stores looking to recover abandoned carts.
Monitoring, Reporting, and Making Data-Driven Adjustments
To ensure your PPC campaigns are continually improving, you need to regularly monitor KPIs
Here are the key metrics to track:
- CTR (Click-Through Rate): Shows how often people click on your ad.
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of clicks that lead to a sale or desired action.
- CPC (Cost Per Click): The average cost of each click.
Scaling Your PPC Campaigns Over Time
As your PPC campaigns start to generate consistent results, it’s time to think about scaling them for even better performance.
Expanding Keyword Lists
As you gain more data, expand your keyword lists to cover more areas of your industry. Let’s say you initially focused on long-tail keywords like “buy organic dog food online” for your pet store. Once you start seeing success with these specific terms, expand to broader keywords such as “organic pet food” or “natural pet care.” This will open the door to a larger audience while still driving relevant traffic.
Launching New Ad Formats
To keep your audience engaged and stay ahead of competitors, consider testing different ad formats:
- Video Ads: If you sell home workout equipment, create short videos showcasing your products in use.
- Shopping Ads: E-commerce businesses can benefit from Google Shopping Ads, where your product photos, prices, and reviews are displayed directly in search results, making it easy for users to compare and click through.
Exploring New Platforms
As you scale, diversify your PPC strategy by advertising on other platforms. For instance, if you’re already seeing good results on Google Ads, expand to Bing Ads or Pinterest Ads. These platforms might have less competition, potentially resulting in lower cost-per-clicks (CPC) and a better Return on Ad Spend (ROAS).
Optimising for Voice Search
With the rise of voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, optimising your PPC campaigns for voice search can give you a competitive edge. Keywords like “best pizza delivery near me” are increasingly popular, and optimising your ads for natural, conversational queries will help capture this growing segment of users.

Measuring Long-Term PPC Success
Finally, the ongoing success of your PPC campaigns relies on careful tracking and analysis.
Measuring ROI
It’s not enough to monitor clicks and impressions. You need to determine if your PPC efforts are yielding a positive return on investment. Use tools like Google Analytics to track which campaigns are driving conversions and revenue and compare those figures against your ad spend.
For example, if you spend $1,000 on PPC ads and generate $3,000 in sales, your ROI is 200%, meaning your campaign is highly profitable. If your ROI is low, it’s time to re-evaluate your strategy—whether that means adjusting your bids, refining keywords, or optimising your landing pages.
Analysing Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
PPC campaigns often focus on immediate conversions, but it’s important to consider the long-term value of a customer. Let’s say you own a subscription-based service, and each new customer is worth $500 over their lifetime. Even if you’re spending $50 to acquire a new customer, that’s a good deal because the long-term profit outweighs the acquisition cost.
By tracking your Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) alongside PPC metrics, you’ll have a more comprehensive view of your campaign’s success.
Staying Updated on PPC Trends
Digital marketing is constantly evolving, and staying on top of the latest trends is key to maintaining your campaign’s performance. Automation tools, AI-driven ad optimisation, and new targeting features are continually being introduced by platforms like Google Ads and Facebook Ads. Regularly revisiting your strategy and incorporating the latest innovations will ensure you stay competitive.
For instance, dynamic search ads are now more sophisticated, automatically generating headlines and targeting based on your website’s content. Adopting these tools can save you time and improve ad relevance.
Conclusion: PPC Campaigns Can Transform Your Business
Pay-Per-Click advertising remains one of the most effective ways to attract high-intent customers and scale your business. Whether you’re running a local service, e-commerce store, or SaaS platform, mastering the steps to set up and optimise a PPC campaign will drive meaningful results.
By continually refining your strategy, testing new approaches, and staying informed on industry trends, your PPC campaigns will not only generate traffic but lead to consistent conversions and revenue growth for your business.